If you are wondering whether you can add external RAM to laptops, Most likely, the answer is “no.” The protocols for working with BIOS, power, and interaction with RAM and external storage are totally different. And you will not get the required performance, even if you somehow manage to forward the device into the system as RAM.
RAM is the main memory of every computer system and provides a large part of the overall performance. However, it cannot be expanded as external storage since no connection would be fast enough for this.
Is External RAM can be used on a laptop?
Frankly speaking, the RAM cannot be used as external storage, as the technical requirements are missing. The main memory is used to quickly supply the processor with data that does not first come from another memory, such as the hard drive must be obtained.
In order to be able to guarantee such a fast data supply, the main memory is installed directly on the mainboard and linked to the processor socket with direct lines. There would also be no interface that could be connected via an external connection, e.g. B. USB would have the ability to accommodate RAM modules. External memory is always slower than internal RAM.
Alternative way
External RAM cannot be added as a required interface, and the specific power supply for RAM is only on the motherboard. However, additional memory (paging files) can be added to Windows by using the flash drive as ReadyBoost. It can be helpful if there is not enough internal RAM.
Increase the memory or RAM using a USB key.
One can increase the RAM using standard USB flash drives with the help of special software. The Microsoft operating system has a specific program module called ReadyBoost, which will help connect the USB flash drive and increase the capacity of your RAM.
You can include up to 8 USB drives; total RAM cannot exceed 256 GB, but not all USB flash drives can be used. They must fulfill the following criteria:
- There must be more than one gigabyte of free space on the USB drive;
- The interface must be USB 2.0;
- The data transfer rate is over 3.5 MB.
As an alternative to a flash drive, one can use another type of memory — cache, like an SD card or SSD. It is important to take into account the novelty of the operating system. In the version of Windows Vista, enabling this RAM will not work.
For a successful start of the process, one must also activate the system’s SuperFetch service.
SuperFetch software involves the process of storing cached information and files, started by the user. This system is automatically included in Windows 7 but, in some cases, can be disabled.
To check this, invoke the system command with the key combination WIN + R. In the search bar that appears, type Regedit. Next, locate the parameter on the left:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
After that, you double-click on the EnableSuperfetch option. Or you will set a numerical value from 1 to 3 (if it is already installed, then everything is fine — The SuperFetch system is activated).
Activation of the USB key
If all the conditions are met, you proceed to the process of activating the USB key as a source of RAM:
- Insert and activate the USB key;
- Go to “My computer” and right-click on the USB key icon;
- In the dialog box, select ReadyBoost;
- In the new window, choose to activate the device for ReadyBoost;
- Below you must choose the amount of memory to use with “ReadyBoost” Choose the maximum value (if the USB key is empty and formatted).
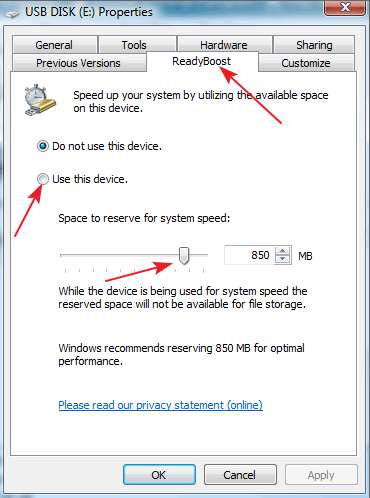
After configuring the cache and restarting your laptop, the operating system will automatically apply the new settings. Important: Do not remove the USB key as long as you need the extra RAM volume.
Note: Before starting the above-described process of increasing RAM using a USB flash drive, format the USB flash drive to remove all possible hidden files.
After that, the USB drive will be displayed in “Computer” with the presence of free memory of 100 megabytes. This space the operating system leaves unused for stable operation of the device; the rest of the memory is occupied with cached files.




![Best Gaming PC Build under $1000 in 2025 [RX 7700XT]](https://www.geeksdigit.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/best-gaming-pc-build-under-1000-336x220.jpg)
